Sugar is usually maligned for a bunch of power well being issues, most notably coronary heart illness. Not solely can consuming an excessive amount of stand in the best way of your aim to drop extra pounds, however it will probably additionally crowd out good-for-you, nutrient-rich meals out of your weight-reduction plan.
Regardless of the warnings, many individuals nonetheless overdo it. âThe typical every day sugar consumption within the U.S. is 73 grams, or 17.4 teaspoons, which has declined considerably in recent times, however continues to be properly above optimum ranges,â says Margaret W. Eich, RD, creator of “Breaking the Sugar Behavior.â On this case, she follows the American Diabetes Affiliation and American Coronary heart Affiliationâs tips, that are not more than 24 grams (6 teaspoons) and 36 grams (9 teaspoons) per day for men and women, respectively.
Itâs useful to study precisely what sugarâs doing within the physique â from the very first chew â that will help you create more healthy habits and meet your diet targets.
HOW YOUR BODY BREAKS DOWN SUGAR
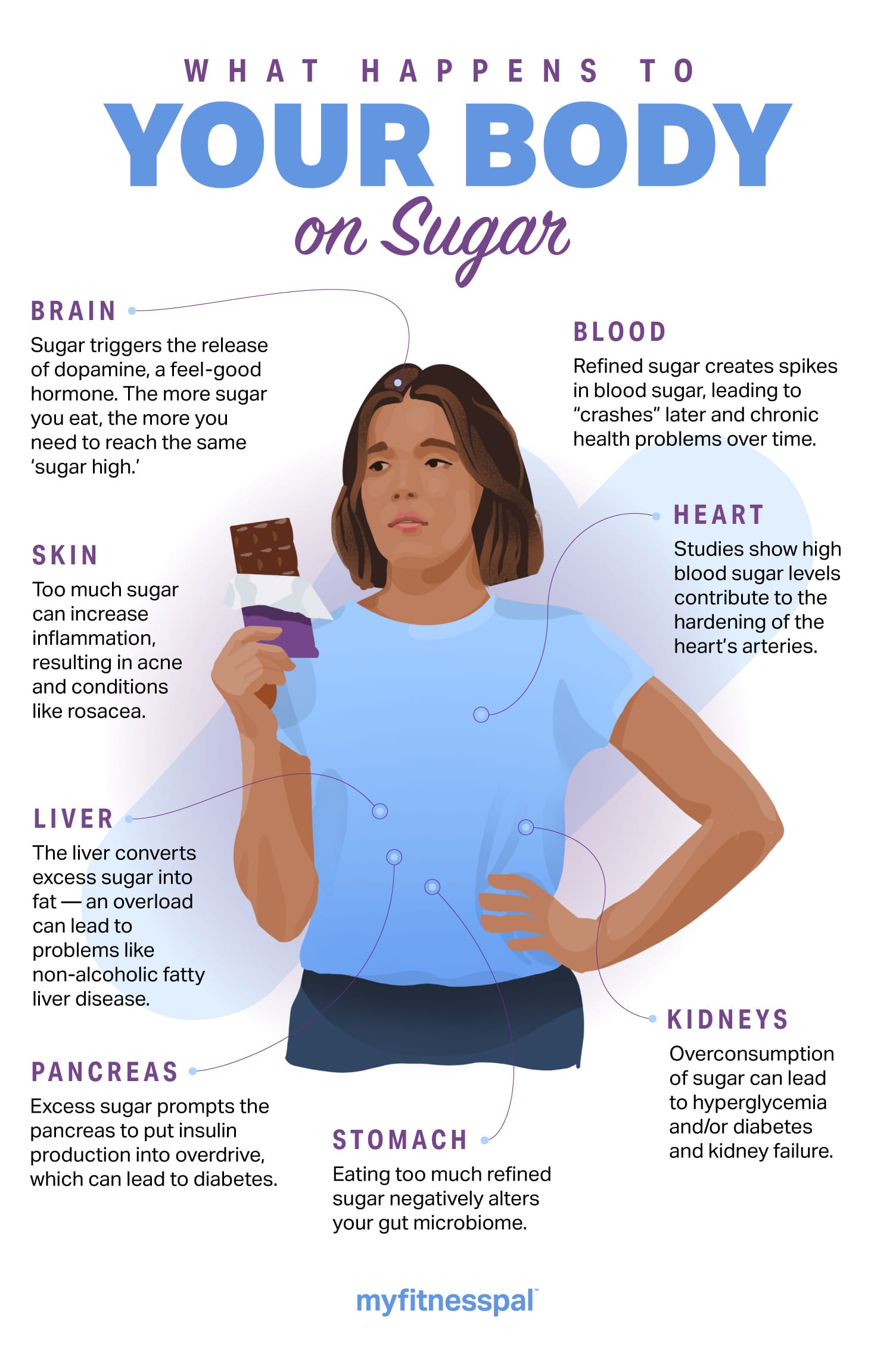
Eat cookies, ice cream, sweet or any variety of delectable treats and your physique breaks down the added sugar it comprises into glucose and fructose. âGlucose is handled in a different way within the physique than fructose,â says Eich. Glucose is an easy sugar or monosaccharide and the constructing block of carbohydrates, the physiqueâs most well-liked supply of power. âGlucose is absorbed instantly into the bloodstream for use as power,â explains Eich. Fructose (typically referred to as fruit sugar), however, is processed within the liver, the place it needs to be transformed to glucose earlier than it may be used as power. This isn’t often an issue in the event youâre consuming fruit, for instance, as a result of the fiber and vitamins assist gradual absorption and preserve blood sugar ranges secure. Nonetheless, fructose is usually present in processed meals (assume high-fructose corn syrup) and when eaten in extra, the liver converts it into fats. This may have destructive results on triglyceride (a sort of fats in your blood) ranges and is a marker of coronary heart illness.
WHY YOUR BODY ASKS FOR MORE
Because of the blood sugar surge and subsequent crash, you may discover you want one other handful of sweet from the workplace bowl to really feel âgoodâ once more. The method âtypically interprets to a dip in temper and power ranges, relying on the individual and quantity of sugar consumed,â says Eich. Sugar is usually regarded as addictive, as a result of the mind adapts to the dopamine (âfeel-goodâ chemical compounds) launched every time you devour sugar. This implies youâll require extra sugar to attain that very same sugar excessive. âIt may possibly typically carry over into subsequent days the place you proceed to crave sugar,â says Eich.
HEALTH PROBLEMS IN THE LONG-TERM
We are likely to deal with how overconsuming processed meals containing extra sugar might contribute to weight achieve or make it troublesome to drop extra pounds, however the dangerous results are even larger. Extra sugar places the pancreas into overdrive (which might result in diabetes) and hardens the centerâs arteries (elevating the danger of coronary heart illness). It additionally raises blood strain and lowers âgoodâ HDL ldl cholesterol,â says Eich. Lastly, analysis reveals an excessive amount of sugar can alter your mindâs chemistry and lead to an elevated threat of despair.
THE BOTTOM LINE
Itâs essential to keep in mind that not all sugar is created equal. Sugar is a pure element of meals like fruits, veggies, dairy merchandise and grains. If you eat these entire meals, you additionally get a plethora of vitamins like nutritional vitamins, minerals, protein, fats and hydrating water. You additionally get fiber, which helps gradual digestion and tempers the discharge of sugar into the bloodstream, stopping these aforementioned crashes. Attempt utilizing an app like MyFitnessPal to watch your sugar consumption, assist you to prioritize entire meals and reduce on added sugar present in processed ones.















